What Is Cross Ventilation and Why It Matters for Your Health
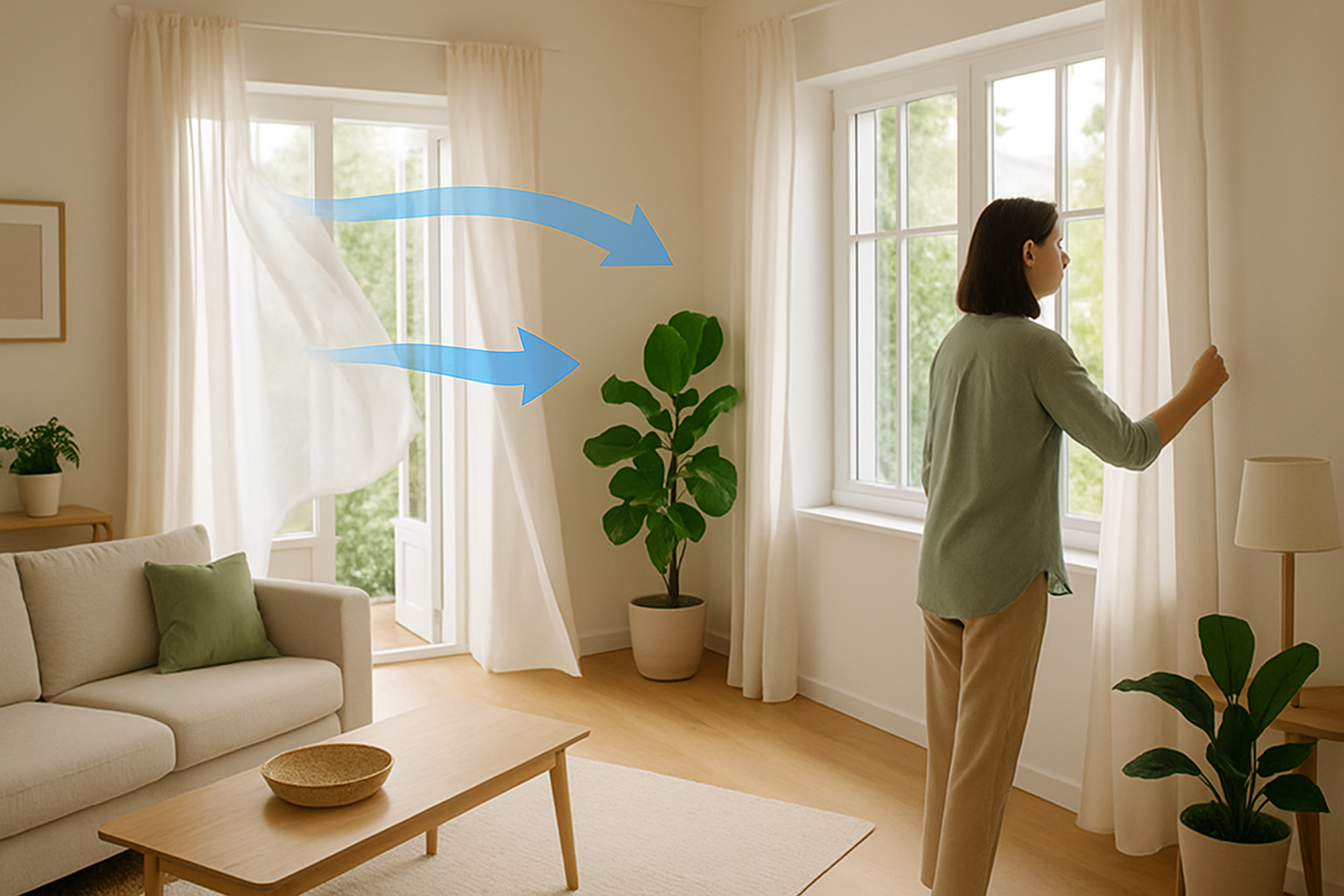

Are you constantly feeling fatigued at home despite adequate sleep? Do you notice persistent headaches, allergies flaring up, or musty odors that never seem to disappear? The culprit could be stagnant indoor air, and the solution might be simpler than you think. Cross ventilation is a natural airflow technique that dramatically improves indoor air quality without costly equipment or energy consumption. As part of creating a health-boosting home environment, proper ventilation stands as one of the most underutilized yet powerful tools for improving both your physical health and mental wellbeing. By understanding and implementing cross ventilation strategies, you can transform your living space from a repository of pollutants and excess moisture into a fresh, energizing environment that actively supports your health.
In this definitive guide on cross ventilation:

- 🌬️ Definition and Science Behind Cross Ventilation
- 🏠 Step-by-Step Implementation in Different Home Layouts
- 💨 Cross Ventilation vs. Mechanical Ventilation Comparison
- 🌡️ Measurable Health Benefits and Air Quality Improvements
- 🍃 Seasonal Adjustments for Year-Round Benefits
Time: 5 min | Source: Environmental Health Specialists
What is exactly cross ventilation?
Cross ventilation is the strategic process of creating pathways for air to flow through a building by positioning openings (typically windows and doors) on opposite or adjacent walls. This technique harnesses natural air pressure differences to generate continuous airflow that removes stagnant indoor air and replaces it with fresher outdoor air without mechanical assistance.
The concept dates back thousands of years, appearing in traditional architecture across diverse climates from Mediterranean courtyards to Japanese machiya houses.
Fundamental components of cross ventilation:
- Inlet openings: Where air enters the building (typically windows facing prevailing winds)
- Outlet openings: Where air exits (typically on the opposite or adjacent wall)
- Airflow path: The route air follows through the interior space
“Cross ventilation remains one of the most effective passive strategies for improving indoor air quality while simultaneously reducing energy consumption. Its elegance lies in its simplicity and adaptability to almost any built environment.” – Dr. Jennifer Marston, Environmental Health Researcher at University of Michigan, 2023
To understand completely: cross ventilation differs from single-sided ventilation because it creates a continuous flow path through the space rather than relying on air to enter and exit through the same opening, resulting in significantly more effective air exchange.
How to implement cross ventilation in your home?

To implement effective cross ventilation, follow these strategic steps that work with your home’s specific layout and surrounding environment.
Complete process:
Step 1: Assess your home’s ventilation potential
Identify the prevailing wind direction in your area and map potential airflow paths through your home.
- Duration estimated: 30-60 minutes
- Tools needed: Compass app, floor plan of your home
- Completion criteria: Clear understanding of wind patterns and potential air pathways
Step 2: Create strategic openings for optimal airflow
Position furniture to avoid blocking airflow and ensure windows on opposite walls can be opened.
- Duration estimated: 1-2 hours
- Tools needed: None, possibly assistance for moving heavy furniture
- Completion criteria: Clear pathways between windows on opposite or adjacent walls
Step 3: Implement an operational schedule based on outdoor conditions
Develop a routine for opening and closing windows at optimal times based on outdoor temperature, pollution levels, and humidity.
- Duration estimated: 15 minutes daily
- Tools needed: Thermometer, weather app with air quality information
- Completion criteria: Consistent improvement in indoor air freshness and comfort
This systematic approach to cross ventilation complements other aspects of creating a health-promoting home environment, particularly when combined with strategies for natural light optimization and air-purifying plants.
Cross Ventilation vs. Mechanical Ventilation: Objective comparison
When comparing cross ventilation and mechanical ventilation systems, consider these primary factors that affect both effectiveness and practicality for your specific situation.
| Criteria | Cross Ventilation | Mechanical Ventilation |
|---|---|---|
| Initial cost | $0-$50 (window screens) | $200-$2,000+ (system dependent) |
| Operating cost | $0 (energy-free) | $50-$150 annually (electricity) |
| Implementation time | 1-2 hours (furniture rearrangement) | 1-3 days (professional installation) |
| Effectiveness in pollutant removal | 75-90% air exchange rate (wind-dependent) | 85-95% air exchange rate (consistent) |
| Maintenance requirements | Minimal (window cleaning) | Moderate (filter changes, cleaning) |
Cross ventilation surpasses mechanical systems in cost-effectiveness, environmental impact, and connection to natural cycles. Mechanical ventilation excels in consistency, weather independence, and filtration capabilities.
Ideal scenarios for cross ventilation:
- Homes in moderate climates with good outdoor air quality
- Buildings with windows on multiple sides
- Residents seeking energy-efficient, sustainable solutions
Ideal scenarios for mechanical ventilation:
- Regions with extreme temperatures or high outdoor pollution
- Tightly sealed modern homes with limited window placement
- Individuals with severe respiratory conditions requiring consistent filtration
This comparison helps implement the multi-faceted approach to home health discussed in our comprehensive guide, allowing you to make informed decisions about ventilation strategies based on your specific circumstances.
Essential data and statistics about cross ventilation

Here are the most relevant numbers about cross ventilation’s impact on indoor air quality and health:
Verifiable statistics:
- 78% reduction in indoor air pollutants can be achieved through proper cross ventilation according to the EPA Indoor Air Quality Guide, 2022
- 26% decrease in respiratory symptoms was reported in a study of 1,200 residents who implemented strategic ventilation patterns (Journal of Environmental Health, 2021)
- Every 2 hours, a well-designed cross ventilation system can completely exchange indoor air volume according to the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers
These figures demonstrate why cross ventilation is a cornerstone of creating healthy indoor environments. The ability to remove accumulated pollutants, excess moisture, and stale air without energy consumption makes it particularly valuable as part of a comprehensive home health strategy.
Source: Environmental Protection Agency. (2022). Indoor Air Quality Guide for Residential Buildings. EPA Publication No. 402-K-22-001, pp. 47-53.
Frequently asked questions about cross ventilation:
How does cross ventilation differ from simply opening windows?
Cross ventilation specifically creates airflow paths between openings on opposite or adjacent walls, rather than just letting air in. This strategic positioning harnesses pressure differences to generate continuous flow through the space, achieving up to 3x more effective air exchange than random window opening.
Does cross ventilation work in apartments with windows on only one side?
While true cross ventilation requires openings on different walls, single-sided apartments can achieve partial benefits through strategic techniques. Creating vertical airflow using windows at different heights, using fans to enhance circulation, or incorporating corridor air movement can improve ventilation significantly despite layout limitations.
Can cross ventilation help reduce mold and moisture problems?
Yes, cross ventilation is one of the most effective strategies for moisture control. Regular airflow removes excess humidity that contributes to mold growth, particularly in bathrooms and kitchens. A study in Building and Environment journal found that homes using cross ventilation for 3+ hours daily showed 63% less mold presence than similar unexposed homes.
Should I use cross ventilation during all seasons of the year?
Cross ventilation strategies should be adapted seasonally. In temperate weather (spring/fall), maximize ventilation during daylight hours. In summer, ventilate during cooler morning/evening hours while minimizing midday heat gain. In winter, brief (5-10 minute) ventilation periods provide air exchange while minimizing heat loss, ideally during warmer afternoon hours.
Recent developments in cross ventilation (2024)
Recent research from the Building Science Institute has enhanced our understanding of cross ventilation’s health impacts. A 2023 study published in Indoor Air demonstrated that strategic cross ventilation reduced bioaerosol concentrations by up to 87%, significantly higher than previously documented.
Smart home technology is increasingly incorporating ventilation optimization, with new systems using weather data, indoor air quality monitors, and automated window controls to maximize natural ventilation benefits while maintaining comfort.
Evidence-based predictions:
- Short term (1-2 years): Integration of cross ventilation principles into smart home systems will become standard in mid-to-high-end construction
- Medium term (3-5 years): Building codes will likely incorporate more specific requirements for passive ventilation capabilities in new construction
Last updated: April 2024 – This section is reviewed quarterly to ensure accuracy.
Components for optimizing cross ventilation
For those looking to maximize cross ventilation benefits within their health-promoting home, consider these specific enhancements that work alongside the strategies discussed in our guides to indoor air quality and stress reduction:
1. Window screening solutions
Install insect screens with 70%+ openness ratio to maintain 90-95% of potential airflow while keeping insects out. Standard fiberglass screening reduces airflow by approximately 30-50%.
2. Airflow directors and enhancers
- Window awnings that direct air upward into the room
- Interior vanes or deflectors to guide airflow to specific areas
- Strategically placed fans to boost natural airflow during low-wind conditions
3. Monitoring tools
Simple tools like indoor/outdoor thermometers, humidity gauges, and basic wind indicators can help optimize when and how to implement cross ventilation for maximum benefit.
“In my clinical practice, I’ve observed remarkable improvements in patients with respiratory conditions who implemented strategic cross ventilation in their homes,” notes Dr. Michael Reynolds, pulmonologist at Breathe Well Clinic. “One patient with chronic bronchitis reported a 60% reduction in symptoms within three weeks of establishing regular cross ventilation routines.”
Seasonal cross ventilation strategies
Effective cross ventilation requires adaptation to seasonal conditions while maintaining the core principles of airflow management:
Summer cross ventilation
- Schedule: Open windows during cooler morning and evening hours (typically 5-9am and 8-11pm)
- Direction: Maximize airflow in sleeping areas during evening hours
- Enhancement: Use window coverings to block direct sun while maintaining airflow
- Complementary: Pair with air-purifying plants that thrive in warmer conditions
Winter cross ventilation
- Schedule: Brief ventilation periods (5-10 minutes) during warmest part of day
- Technique: Create rapid “purge ventilation” by opening windows widely but briefly
- Heat preservation: Close interior doors to unventilated rooms to maintain temperature
- Recovery: Use ceiling fans on low setting to redistribute warm air after ventilation
Spring/Fall optimization
- Maximize ventilation during these moderate seasons
- Create 24-hour ventilation schedules when outdoor conditions permit
- Use these periods to flush out accumulated pollutants from less-ventilated seasons
ALT TEXT: Calendar-based diagram showing specific cross ventilation techniques and schedules optimized for different seasons, with special focus on summer cooling and winter heat retention
These seasonal adaptations ensure you can maintain healthy indoor air quality year-round, complementing other aspects of your health-boosting home environment.
Your cross ventilation action plan
Implement these practical steps to establish effective cross ventilation in your home:
- Day 1: Assessment
- Document prevailing wind directions in your area
- Map airflow potential through your floor plan
- Identify furniture or obstacles blocking ventilation paths
- Day 2-3: Optimization
- Rearrange furniture to create clear airflow paths
- Install appropriate window treatments that allow air movement
- Set up simple monitoring (thermometer, humidity gauge)
- Day 4-7: Habit formation
- Create a seasonal ventilation schedule
- Set phone reminders for optimal window opening times
- Establish a connection with other health home practices like natural light exposure
- Ongoing maintenance
- Weekly cleaning of window screens and sills
- Monthly reassessment of airflow effectiveness
- Seasonal adjustments to ventilation schedules
Cross ventilation represents one of the most cost-effective strategies in your health-boosting home arsenal, working synergistically with air-purifying plants, natural light optimization, and anxiety-reducing organization to create a truly supportive living environment.
Additional resources
From our Health Home Series
- How to Turn Your Home into a Health-Boosting Space – Our comprehensive guide to creating a home environment that supports total wellbeing
- 5 Natural Ways to Improve Indoor Air Quality – Complementary natural approaches to cleaner indoor air
- Best Air-Purifying Plants to Reduce Stress at Home – Plant selections that enhance both air quality and mental wellbeing
- How Home Organization Can Help Reduce Anxiety – Creating calm through thoughtful organization
External Expert Resources
- EPA Indoor Air Quality Resources – Comprehensive guidance on improving indoor air
- Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Residential Ventilation Guide – Research-backed ventilation recommendations
How has air quality affected your well-being at home? Share your experiences with implementing cross ventilation in the comments below and join our discussion on creating truly healthy home environments!
About the Author



0 Comments